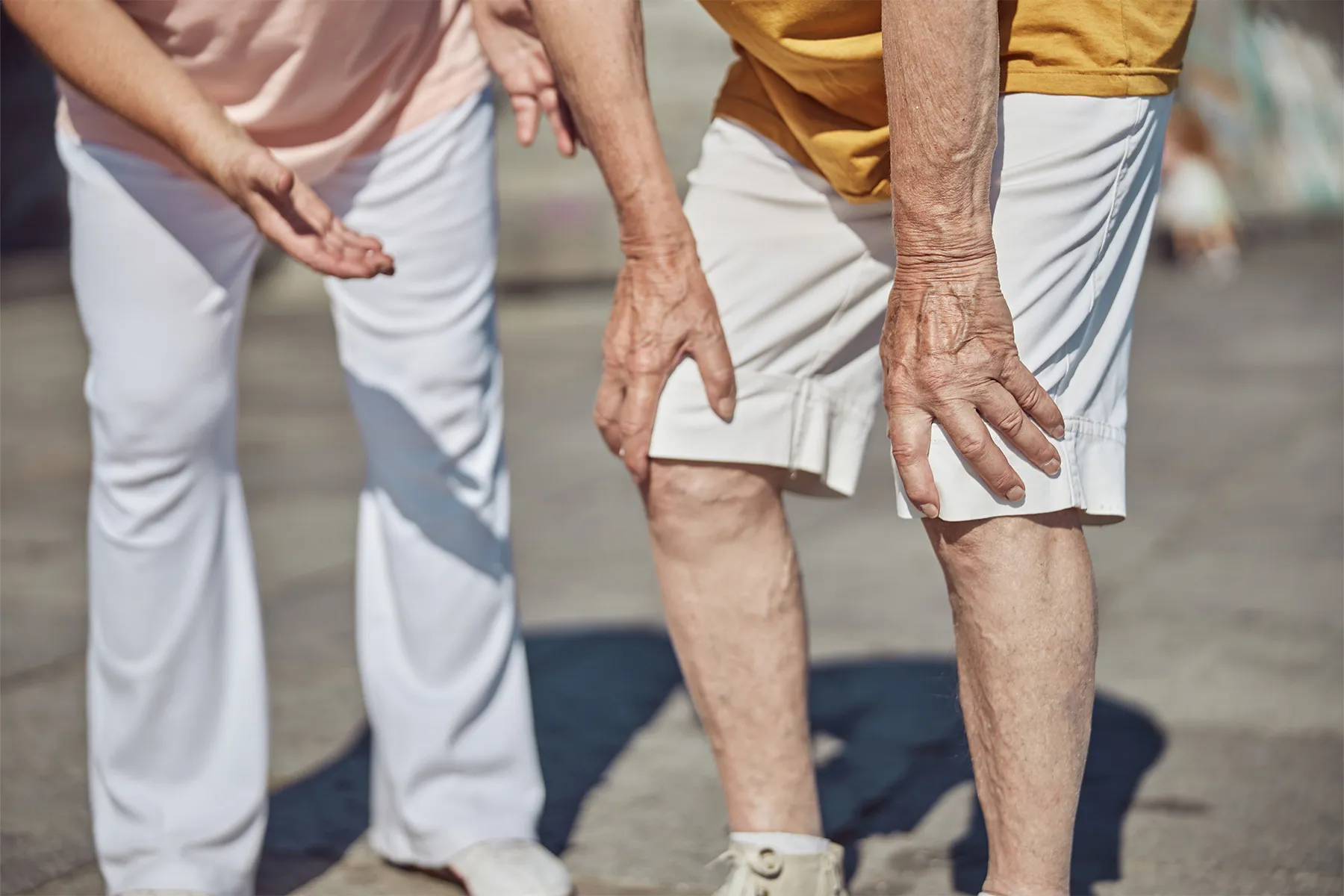
Have you ever experienced a sudden sharp pain in your calf while sleeping? While an occasional "charley horse" during the night can certainly be a nuisance, for others, leg cramps are a common and painful occurrence often linked to vein health.
Understanding this connection is an important step in effectively managing and preventing leg cramps, especially for those experiencing them frequently. This article will explore the relationship between leg cramps and vein circulation problems, and provide tips and prevention strategies to improve vascular health and reduce unpleasant leg cramping.
Understanding Leg Cramps: Types and Causes
Leg cramps involve involuntary muscle contractions, often in the calf. These cramps, particularly nocturnal ones, can impact your quality of life and sleep. They are several common causes of leg cramps, including circulation problems, muscle fatigue, and electrolyte imbalances.
There are two types of causes of leg cramps, primary and secondary.
- Primary cramps are idiopathic (unknown cause)
- Secondary cramps stem from underlying health conditions.
Recognizing the connection between leg cramps and vein health can often lead to better management of symptoms and more effective treatment options. Some common causes of leg cramps include:
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Occurs when your veins can't efficiently pump blood back to your heart.
- Common Lifestyle Triggers: Dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and muscle strain can also trigger cramps.
- Claudication: Develops when the arteries that supply blood to your legs become blocked.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Another medical condition associated with vein health, PAD occurs when narrowed arteries reduce the blood flow to the arms and legs.
The Vein-Cramp Connection
There is a clear correlation between vascular disease and frequent leg cramps. This is because, for those diagnosed with chronic venous insufficiency, veins struggle to return blood to the heart, leading to problems with circulation. When inadequate blood flow prevents adequate oxygen and nutrients from being delivered to the muscle cells, cramping can occur.

Nocturnal Leg Cramps: A Vascular Perspective
Leg cramps and restless legs often occur at night due to fluid redistribution and changes in vein function. During sleep, fluid shifts can affect electrolyte balance and circulation. Nighttime cramps is a common cause of disrupted sleep, which can reduce overall quality of life.
Preventing Nighttime Cramps
Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy balance of electrolytes are two easy things you can do at home to help ward off nighttime leg cramps. Elevating your legs before bed and wearing compression stockings during the day can also help reduce the frequency of leg cramps at night.
Treating underlying vein health issues can also reduce and even resolve this annoying (and uncomfortable) symptom. Make sure to discuss the frequency of leg cramps with your vein specialist.
Warning Signs: When Cramps Indicate Vein Problems
The frequency and duration of leg cramps, in addition to other associated symptoms, can indicate a vein-related issue. Warning signs to look out for include:
- Cramping Patterns: Leg cramps that worsen with prolonged standing or at night may indicate venous insufficiency.
- Symptoms of Vein Disease: Swelling, varicose veins, and skin changes should be evaluated and monitored by a vein specialist.
- Progression of Vein Disease: Untreated vein disease can lead to more frequent and severe leg cramping.
Emergency Warning Signs
Seek immediate medical attention if cramps are accompanied by any of the following severe symptoms:
- Serious Vascular Issues: Sudden leg swelling, pain, or discoloration.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Chest pain and shortness of breath alongside leg symptoms.
- Arterial Compromise: Severe pain and coldness in the leg.
Varicose Veins and Cramping Mechanisms
Varicose veins contribute to leg cramping through valve dysfunction and blood pooling in the following three ways:
- Valve Dysfunction: Damaged valves lead to blood pooling, increasing pressure and cramping.
- Inflammation Pathways: Inflammation in vein walls can trigger muscle spasms.
- Pressure Changes: Increased venous pressure affects surrounding tissues, causing pain and cramping.

Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing vein-related leg cramps involves thorough physical and vascular evaluations by a vein specialist. These involve:
- Physical Examination: Assessing for signs of venous insufficiency and varicose veins.
- Vascular Evaluation: A Doppler ultrasound is often used to assess blood flow.
- Electrolyte and Mineral Testing: Ruling out other causes like magnesium deficiency.
- Ruling Out Other Causes: It's important to differentiate vein-related leg cramps from neurological or other causes. Your vein doctor can provide you with a definitive diagnosis.
Non-Medication Prevention Strategies
While the only permanent, effective treatment for vein disease is an approved medical treatment, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of leg cramps.
- Hydration Strategy: Staying hydrated can have a beneficial impact on the frequency of leg cramps.
- Optimal Leg Positions: Elevating your legs during the day and avoiding prolonged standing can also help.
- Exercise Approaches: Low-impact exercises can improve circulation.
- Stretching Techniques: Regular stretching can help prevent muscle spasms.
Compression Therapy for Cramp Management
Wearing compression stockings can support vein function by improving blood circulation in your legs. Regular use of medical-grade compression stockings may help relieve symptoms associated with vein disease. Things to consider when beginning compression therapy include:
- Appropriate Compression Levels: Graduated compression is most effective.
- Wearing Schedules: Consistent use during the day and sometimes at night.
- Nighttime Use: Light compression can help with nocturnal cramps. Many medical insurances provide a certain number of free compression stockings each year

Nutritional Support for Vein Health and Cramp Prevention
Maintaining a balanced diet and adequate hydration are lifestyle modifications that can help prevent cramps.
- Hydration, Essential Electrolytes: It's important to stay hydrated and drink electrolyte-rich fluids.
- Minerals: A diet rich in magnesium, potassium, and calcium can also reduce the likelihood of experiencing leg cramps.
- Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Approaches: Reducing processed foods and increasing fruits and vegetables.
- Supplements: Magnesium and potassium supplements may help.
Medical Interventions for Vein-Related Cramping
When lifestyle changes are not enough, medical intervention may become necessary. For expected recovery timelines, symptom improvement will vary based on the procedure and the individual.
Depending on the underlying cause of your symptoms, the following options may be recommended:
- Vein Treatment Procedures: Minimally invasive treatment procedures, like sclerotherapy or radiofrequency ablation. These procedures treat chronic venous insufficiency.
- Medication Approaches: Medications to improve circulation and reduce inflammation.
Special Populations and Considerations
Certain populations and factors may have additional considerations for leg cramps and vein health. These include:
- Athletes: Exercise-induced cramps may have a vein health component.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume can cause leg cramps.
- Older Adults: It is important to address complex causes and comorbidities.
- Standing Occupations: Preventative measures for those with prolonged standing.
Summing it Up
Reducing leg cramps requires an integrated approach that may also require managing vein health issues. Lifestyle changes, compression therapy, and medical Interventions can all significantly improve venous return and reduce leg cramping.
Do you have concerns about symptoms like leg discomfort, including cramping? Book a free vein health evaluation to rule out whether your symptoms are caused by worsening vein disease, because healthy legs feel better!
Frequently Asked Questions
How can you differentiate between leg cramps caused by venous insufficiency versus those caused by electrolyte imbalances?
Cramps caused by venous insufficiency are often associated with swelling and varicose veins, while electrolyte imbalance cramps are more generalized and related to dehydration.
Is there a specific compression stocking strength that works best for preventing vein-related nocturnal leg cramps?
Yes. Your vein specialist can recommend the appropriate compression stockings for you, but graduated compression stockings with moderate pressure (20-30 mmHg) are often recommended.
Can untreated varicose veins lead to progressively worsening nighttime leg cramps, and if so, what is the timeline?
Yes, untreated varicose veins can worsen over time, with cramping increasing in frequency and severity over months to years. This is why early detection of vein disease is so important.
What specific stretching techniques most effectively prevent leg cramps associated with chronic venous insufficiency?
Effective stretching and exercise techniques include calf stretches, hamstring stretches, and ankle rotations.
How long after successful vein treatment procedures (like endovenous ablation) do patients typically experience reduction in leg cramping symptoms?
Most patients experience a significant reduction in cramping within a few weeks to months after any vein treatment procedures.

Dr. Philip LoPresti
Meet Dr. Philip LoPresti DO, DABVLM, FACS, a board-certified vein specialist and surgeon with over 20 years of experience. Schedule an appointment with him in Queens, NY today.
Meet Dr. Philip LoPresti
Trusted insight from the nationally accredited, board-certified vein doctors at Metro Vein Centers.